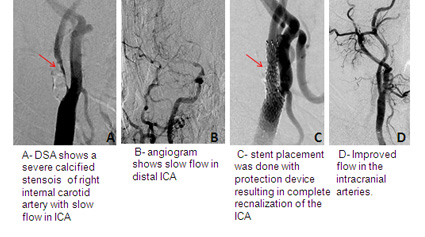
What is the role of carotid artery in stroke?
Stroke is third most common cause of death and disability. According to WHO Survey in 1990, out of 9.4 million deaths in India 6,19,000 were due to stroke. Most of the strokes (approximately 75%) are ischameic in nature and large vessel disease accounts for approximately 40% of ischaemic strokes. It has been estimated that approximately 20-30% of strokes may be caused by stenosis of carotid artery.
What are the various means to diagnose Carotid Artery Stenosis?
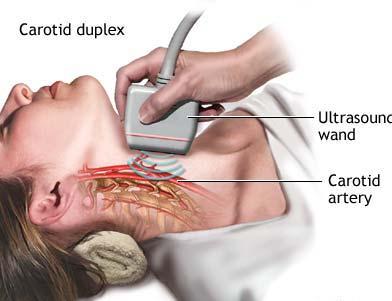
- Carotid Doppler - is a non-invasive & accurate modality to assess carotid stenosis.
- MR angiography (MRA)/CT angiography (CTA)- excellent quality imaging of carotid artery can be done by these relatively non-invasive methods.
- Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the "Gold standard", however it is an invasive investigation and is usually reserved to evaluate stenosis detected in non-invasive investigations as well when the non-invasive investigations are non-conclusive.
What are the treatment options in Carotid Artery Stenosis?
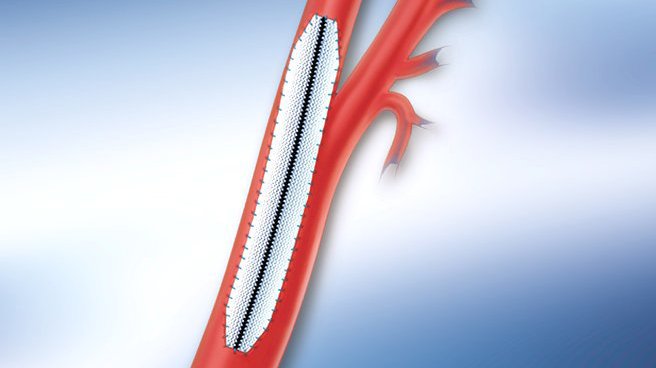
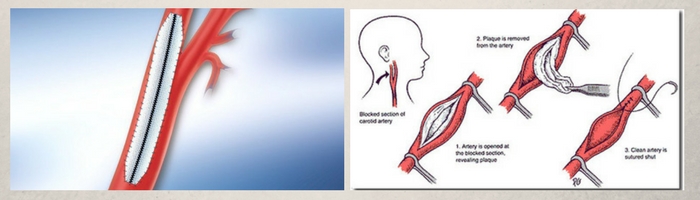
Medical treatment is done for the risk factors for atherosclerosis such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus & dyslipidemia . Patients are also told to stop smoking. Anti-platelet drugs (Dispirin, clopidogrel) are useful to prevent embolic events. Patients with marked stenosis require revascularization which can be achieved by surgical (endarterectomy) or endovascular (angioplasty & stenting) means.
What are the indications for carotid revascularization (stenting/ endarterectomy)?
- Carotid stenosis more than 70%: should be revascularized.
- Carotid stenosis (50%-69%): Revascularization is recommended for patients who have had recent transient ischaemic attack or stroke depending upon patient-specific factors such as age, gender, co morbidities, and severity of initial symptoms.
- Carotid stenosis less than 50%: No benefit of surgery is demonstrated in these patients.
Asymptomatic carotid stenosis:There is no established guidelines on treatment of asymptomatic carotid stenosis. In these patients, transcranial Doppler allows for real time assessment of blood flow in the brain arteries and evaluate for risk of further stroke. Further, assessment for microemboli (small clots that cannot be visualized by other modalities) can be undertaken. Carotid artery stenting is advisable and is offered in high risk patients.
How does carotid stenting compare to surgical endarterectomy?
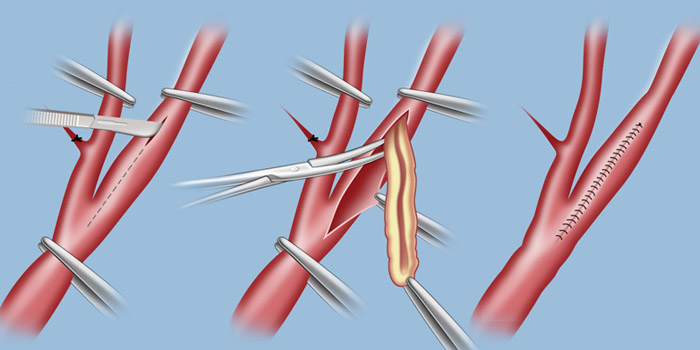
Patients who have coexisting medical problems or advanced age (>80) are better suited for stenting rather than endarterectomy. Patients having certain anatomical features such as prior ipsilateral endarterectomy, prior neck irradiation, contralateral internal carotid artery (ICA) occlusion & high cervical stenosis are also better suited for stenting as compared to endarterectomy.
Patients with marked tortuosity of the common carotid artery and ICA or contraindications to anti-platelet therapy may not be suitable candidates for endovascular therapy.
What is a protection device and what is its role in carotid stenting?
Filter protection devices are umbrella-shaped devices that are placed temporarily in the internal carotid artery beyond the site of stenosis during the procedure. These devices have small pores designed to exclude particulate debris embolization to cranial circulation during the procedure.
Can stenosis of other cranial arteries such as vertebral and intracranial arteries be treated?
Many cases of stroke occur due to stenosis in vertebral & intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Recent studies have shown that these patients with intracranial stenosis have high risk of stroke in spite of medical treatment. Recent advances in technology has made angioplasty and stenting possible in these patients.